In-Built Aggregate Functions
Aggregate Formula allows you to create powerful metrics to address your business needs. In this section let's learn about the wide range of powerful in-built functions that are supported by Zoho Advanced Analytics.
Aggregate Functions
The following table describes these functions:
| Functions | Details |
| Sum | Format:
sum(expr) Description:
The Sum function adds all the values in the expression. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the total value of the numeric expression (expr). Example:
sum("Sales"."Price"-"Sales"."Discount") This calculated the selling price by subtracting the Discount from the Price and then finds the total selling price by adding values for all records. See Also:
avg(), sumif(), avgif() |
| Avg | Format:
avg(expr) Description:
The Avg function finds the average value of the expression's results. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the average value of the numeric expression (expr). Example:
avg("Sales"."Sales"-"Sales"."Cost") This calculated the profit by subtracting the Cost from the Sales for all records and then finds the average of these values. See Also:
sum(), sumif(), avgif() |
| Min | Format:
min(expr) Description:
The Min function finds the minimum value of the expression's results. Parameters: - expr - An expression or a column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the minimum value of the expression (expr). Example: min("Sales"."Amount") This will find the minimum sales done. Note: - Returns null, if the column does not contain any values.
- For string arguments, it compares the ASCII code of the first character of the given string arguments.
See Also:
max() |
| Max | Format:
max(expr) Description:
The Max function finds the maximum value of the expression's results. Parameters: - expr - An expression or a column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the maximum value of the expression (expr). Example: max("Sales"."Amount") This will find the maximum sales done. Note: - Returns null, if the column does not contain any values.
- For string arguments, it compares the ASCII code of the first character of the given string arguments.
See Also:
min() |
| Count | Format:
count(expr) Description:
The Count function identifies the number of rows where the expression's result is present. Parameters: - expr - An expression or a column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the count of rows with the expression's result. Example: count("Sales"."Customer_ID") This will find the total number of rows with a Customer_ID. Note: - Returns null, if the column does not contain any values.
- For string arguments, it compares the ASCII code of the first character of the given string arguments.
See Also:
distinctcount(), count_wb(), countif() |
| Distinct Count | Format:
distinctcount(expr) Description:
The Distinct Count function identifies the number of unique values present in the expression's result. Parameters: - expr - An expression or a column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the count of unique values in the expression's result. Example: count("Sales"."Customer_ID") This will find the total number of customers present in the data. Note: - Returns null, if the column does not contain any values.
- For string arguments, it compares the ASCII code of the first character of the given string arguments.
See Also:
count(), count_wb(), countif() |
| Count_WB | Format:
count_wb(expr) Description:
The Count_WB function identifies the number of rows where the expression's result is present including the null value. Parameters: - expr - An expression or a column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns: This returns the count of rows with the expression's result including the null value. Example: count("Feedback"."email_id") This will find the total number of feedback entries with or without the email address. See Also:
count(), distinctcount(), countif() |
| Stddev | Format:
stddev(expr) Description:
The stddev is a statistical number that measures how spread out the values are. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the standard deviation of the numeric expression (expr). Example:
stddev("Stock"."Price") This returns the standard deviation of the stock price. This helps in measuring the risk involved in the investment. See Also: stddev_samp(), variance(), var_samp() |
| Variance | Format:
variance(expr) Description:
The Variance is another statistical number that measures how spread out the values are. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the standard deviation of the numeric expression (expr). Example:
stddev("Stock"."Price") This returns the variance of the stock price. This helps in measuring the risk involved in the investment. See Also: stddev_samp(), stddev(), var_samp() |
| SumIf | Format:
sumif(condition, expr1 or expr2) Description:
The SumIf calculates the sum of the expr1 or expr2 based on the condition specified. The expr1 or expr2 can be an expression or just a numeric column. Parameters: - condition (Type:Boolean) - The condition that will be evaluated to true or false.
- expr1 - Value to return if the condition is true.
- expr2 - Value to return if the condition is false. This is an optional argument.
Returns:
This returns the sum of expr1, if the condition is true. Else it will return the sum of expr2. Example:
sumif("Sales"."Status"!='Cancelled',"Sales"."Amount",0) This will return the sum of the Amount if the status is not cancelled. Else it will return zero. Note:
In case the expr2 is not provided, it will be taken as null value. See Also:
sum(), avg(), avgif() |
| AvgIf | Format:
avgif(condition, expr1 or expr2) Description:
The AvgIf calculates the average of the expr1 or expr2 based on the condition specified. The expr1 or expr2 can be an expression or just a numeric column. Parameters: - condition (Type:Boolean) - The condition that will be evaluated to true or false.
- expr1 - Value to return if the condition is true.
- expr2 - Value to return if the condition is false. This is an optional argument.
Returns:
This returns the average of expr1 if the condition is true. Else it will return the average of expr2. Example:
avgif("Deals"."Stage" = 'Closed Lost to Competition', "Sales"."Amount") This will return the average deal Amount that is lost to Competition. Note:
In case the expr2 is not provided, it will be taken as null value. See Also:
sum(), sumif(), avgif() |
| CountIf | Format:
countif(condition, expr1 or expr2) Description:
The CountIf calculates the count of the expr1 or expr2 based on the condition specified. The expr1 or expr2 can be an expression or just a numeric column. Parameters: - condition (Type:Boolean) - The condition that will be evaluated to true or false.
- expr1 - Value to return if the condition is true.
- expr2 - Value to return if the condition is false. This is an optional argument.
Returns:
This returns the count of expr1, if the condition is true. Else it will return the count of expr2. Example:
countif("Tasks"."Status" = 'Overdue') This will return the number of task where the status is overdue. Note:
In case the expr2 is not provided, it will be taken as null value. See Also:
count(), distinctcount(), count_wb() |
| YTD | Format:
ytd(aggexpr, date_column, fiscal_start_Month [Optional]) Description:
The Year-to-Date filters the period, starting from the beginning of every year and ends at the current date of the respective year. Parameters: - aggexpr - An Aggregate expression (like SUM, AVG, ... ) for which the Year to Date value will be calculated.
- date_column - A date column based on which Year-to-Date will be calculated.
- fiscal_start_Month - The starting month of the fiscal year. Value ranges from 1(1=Jan,2=Feb) to 12, null(if not required). This is mandatory only if you set a different fiscal start month in your workspace.
Returns:
This returns the result of the aggexpr for the filtered period. Example:
ytd( sum("Sales"."Sales"),"Sales"."Date") Let's assume that the current date is 17th March 2019. This formula will return the sum of sales for all years till 17th March of that year. See Also:
mtd(), qtd() |
| QTD | Format:
qtd(aggexpr, date_column, fiscal_start_Month [Optional]) Description:
The Quarter-to-Date filters the period, starting from the beginning of every quarter and ends at the same quarter's nth day nth month of current date. Parameters: - aggexpr - An Aggregate expression (like SUM, AVG, ... ) for which the Quarter-to-Date value will be calculated.
- date_column - A date column based on which Quarter-to-Date will be calculated.
- fiscal_start_Month - The starting month of the fiscal year. Value ranges from 1(1=Jan,2=Feb) to 12, null(if not required). This is mandatory only if you set a different fiscal start month in your workspace.
Returns:
This returns the result of the aggexpr for the filtered period. Example:
qtd( sum("Sales"."Sales"),"Sales"."Date") Let's assume that the current date is 17th March 2019 and you have the calendar year as your fiscal year. This formula will return the sum of sales for all quarters till 17th of the last month of the quarter. See Also:
mtd(), qtd() |
| MTD | Format:
mtd(aggexpr, date_column, fiscal_start_Month [Optional]) Description:
The Month-to-Date filters the period, starting from the beginning of every month and ends at the current date of that month. Parameters: - aggexpr - An Aggregate expression (like SUM, AVG, ... ) for which the Month-to-Date value will be calculated.
- date_column - A date column based on which Month-to-Date will be calculated.
- fiscal_start_Month - The starting month of the fiscal year. Value ranges from 1(1=Jan,2=Feb) to 12, null(if not required). This is mandatory only if you set a different fiscal start month in your workspace.
Returns:
This returns the result of the aggexpr for the filtered period. Example: mtd( sum("Sales"."Sales"),"Sales"."Date") Let's assume that the current date is 17th March 2019. This will return the sum of sales for the all months till the 17th of that month. See Also:
ytd(), qtd() |
| Mean | Format:
mean(expr) Description:
The Mean is the average calculated by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of rows. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the average value of the numeric expression (expr). Example:
mean("Deals"."Amount") This returns the average deal amount by adding all deal amount and divide it by the number of deals. See Also:
median(), mode() |
| Median | Format:
median(expr) Description:
The Median is the average calculated by ordering the values from least to greatest and identify the middle value of the data. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This orders the result of the numeric expression (expr) in ascending order and returned the middle value. Example:
median("Deals"."Amount") This will order the deal amount from least to greatest and return the middle value. See Also:
mean(), mode() |
| Mode | Format:
mode(expr) Description:
The Mode is the most frequently occurring value. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
Returns:
This returns the value that occurs most often in the expression's result. Example:
mode("Tickets"."Number of Responses") This will return the Number of Responses taken to close most of the tickets. See Also:
mean(), median() |
| Percentile | Format:
percentile(expr, range) Description:
The Percentile identifies a value where a certain percentage of value falls below that number. Parameters: - expr - A numeric expression or a numeric column over which the function is to be applied.
- range - A number to specify the percentage of the column values that should fall below the Percentile value. e.g., the 90th percentile of an expression is a number that has 90% of the values below it. Value ranges from 0 to 100.
Returns:
This returns a value below which the specified percentage of the expression (expr) value lies. Example:
percentile("Sales"."Amount", 90) This will identify a sales value below which 90% of the sales amount lies. |
Groupby Shifting Expressions
By default, Aggregate Formula values will be computed for each data record/group in a report in which it is used. However, to meet your specific requirements, you can also specify how a column's data is to be grouped for computing the values.
The Groupby Shifting Expressions give you more control over how the columns are grouped to compute the values. Zoho Advanced Analytics allows you to perform this in the following levels.
Include Groupby
The Include Groupby formula allows you to add more dimensions to a group by clause, along with the existing dimensions used, in the report where this Aggregate Formula is used.
Format
AggExpr(include_groupby(AggExpr, Column-to-Include)
Example
avg(include_groupby(sum("Orders"."Total Price"), "Customers"."Full Name"))
In the above expression, we calculate the average of Sales per Customer. The Sum of Sales is first grouped by Customer Name, along with the existing group by columns in the report. This will get the total sales for each customer. Now the average of these values will be displayed in the report i.e., the average of Orders per Customer.
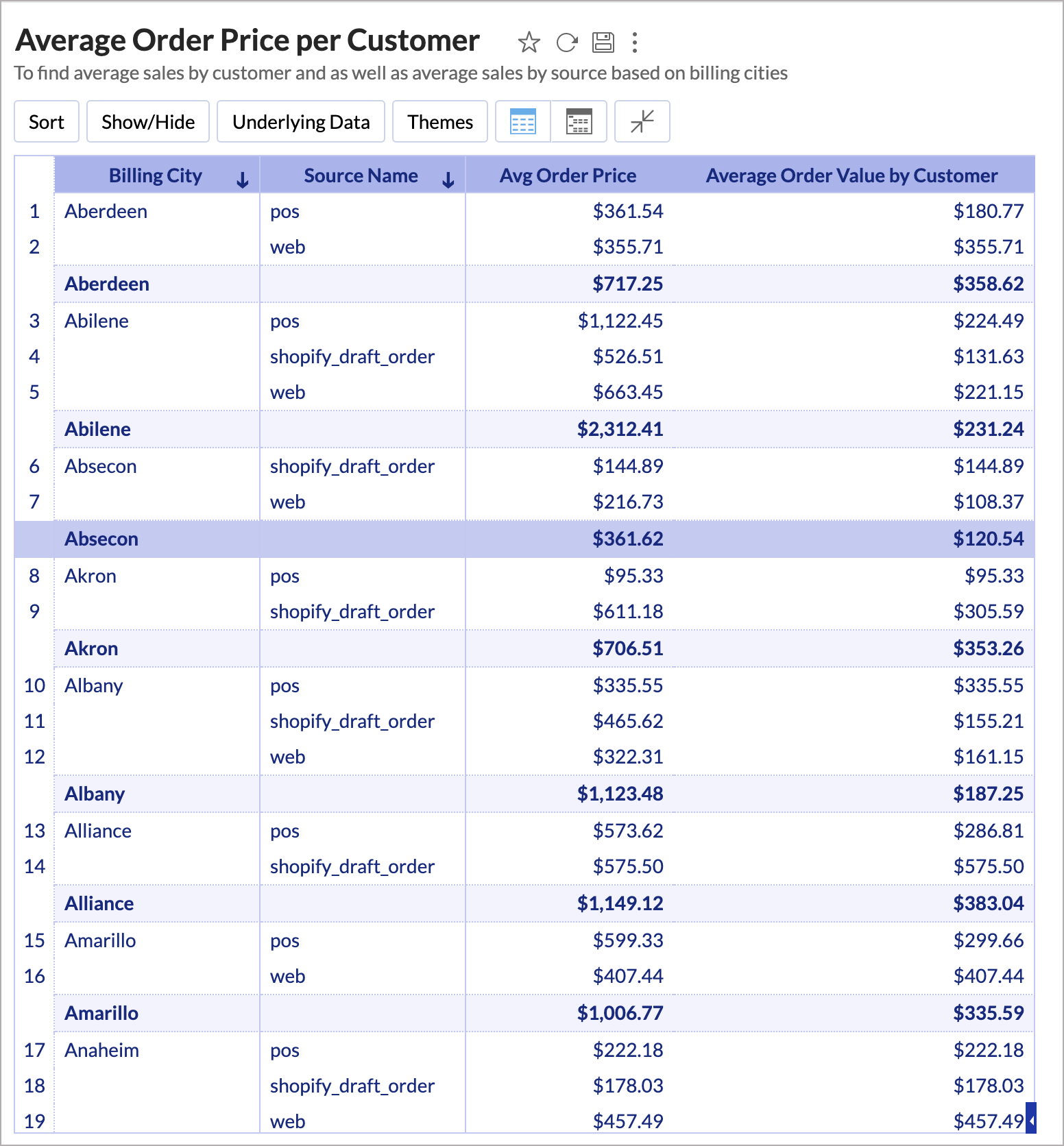
In the above chart, the Avg Order Price column shows the total sales average based on source. The aggregate formula Avg Order Value by Customer shows the average sales made by a customer.
Exclude Groupby
Exclude Groupby allows you to omit or ignore group by dimensions, that are available in the report when aggregate values are computed.
Format
Exclude_Groupby(AggExpr, Column-to-Exclude)
Example
Exclude_Groupby(sum("Orders"."Total Price"), "Orders"."Source Name")
Here, if the report is grouped by Source Name, then the above expression will exclude for calculating the sum of Sales.
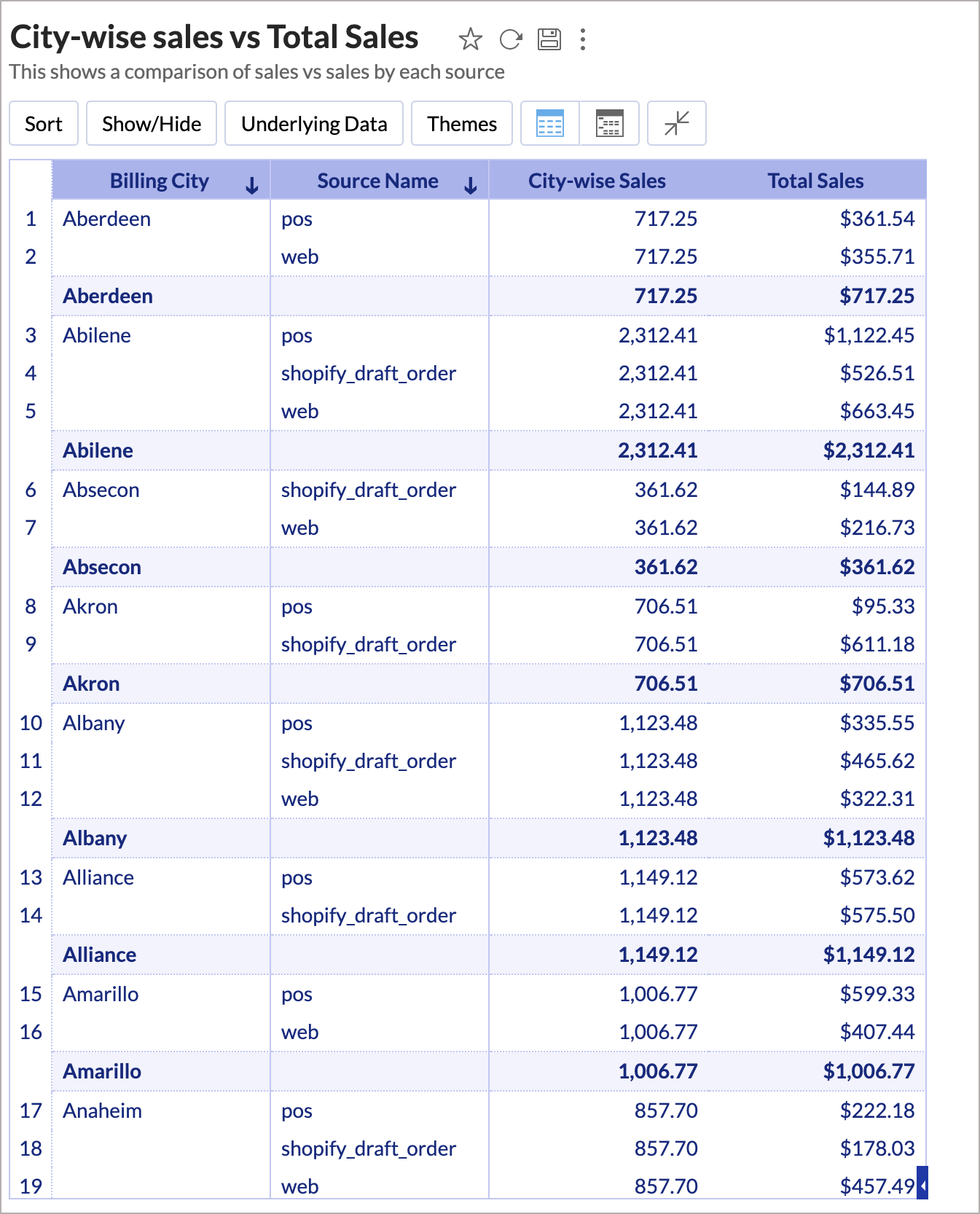
In the above chart, the City wise sales column shows the total sales of each city based on the order source. And the aggregate formula shows the total sales based on order source ignoring the Billing City field in the report.
Fixed Groupby
Fixed Groupby allows you to set a specific group by dimensions to compute values, independent of the group by dimensions available in the report.
Format
AggExpr(fixed_groupby(AggExpr, Fixed-Column-to-compute)
Example
Avg(Fixed_Groupby(sum("Orders"."Total Price"),absquarter("Orders"."Created At")))
Here, irrespective of whatever grouping is done in the report, data will be grouped by the absolute quarter of the Created At column to compute the sum of Total price. i.e., irrespective of the Regional grouping in the report, the formula will calculate the quarterly sales.
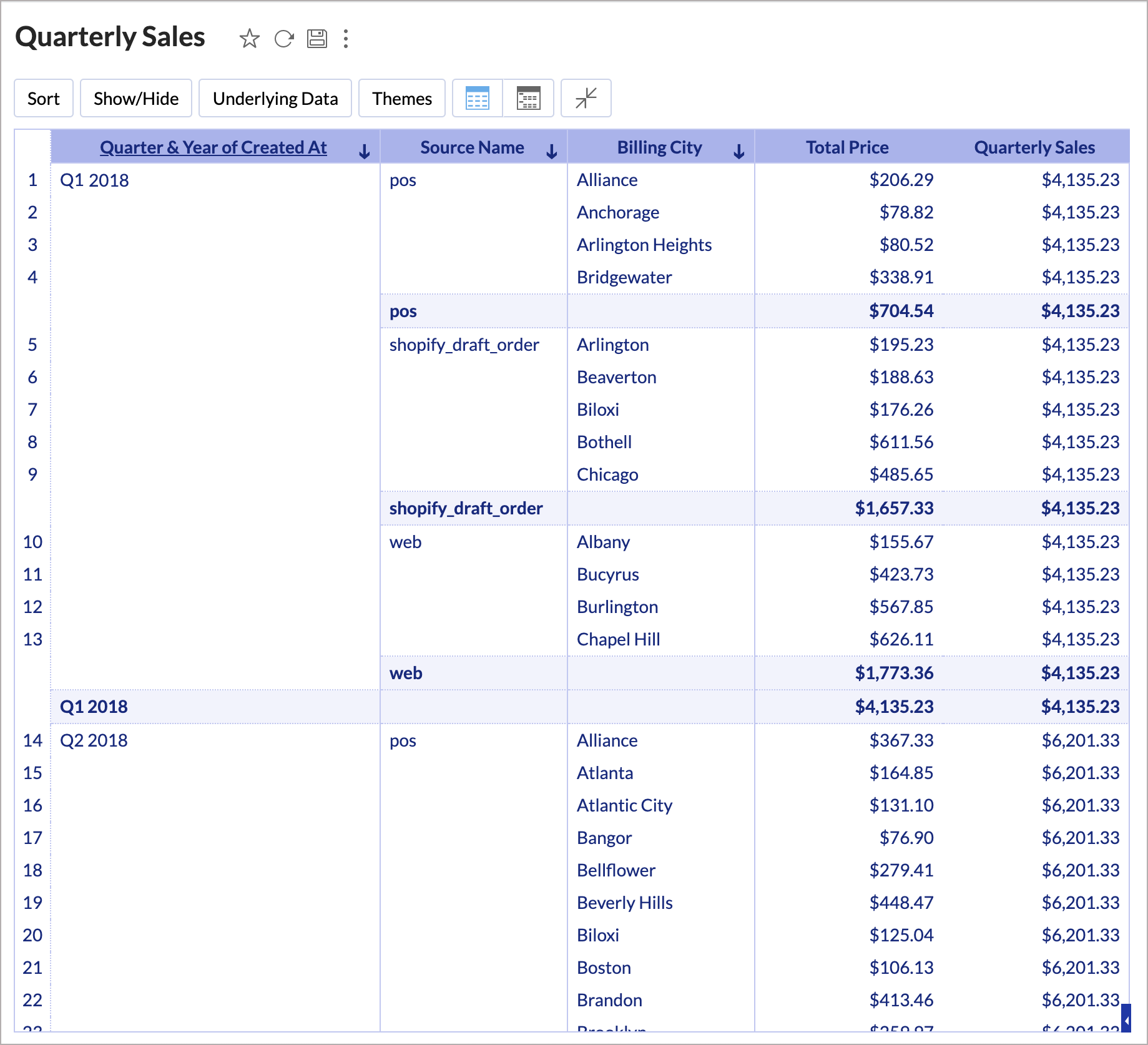
In the above chart, theTotal Sales shows the sales for the dimension in the chart. The aggregate formula Quarterly Sales shows the sales in each quarter irrespective of the dimension used in the report.
Map Groupby
This Map Groupby maps a group by column with another. When you use the first group by column in the report, the aggregate expression will be calculated based on the mapped column instead of the column in the report.
Format
Map_Groupby(AggExpr, "Column in Report", "Column to Map")
Example
Map_Groupby(sum("Orders"."Total Price"),"Orders"."Created At","Orders"."Closed At")
In the above expression, when you add Closed At as a dimension in your report, the sum of delivered sales will be calculated based on the Closed At instead of Created At.
In the above chart, the total sales gets the sales amount for all orders received based on Created At and Sales on End Date gets the sales amount for delivered orders based on delivered date.
The Ignore Filters formula will ignore all the user filters based on the specified column. for the calculated aggregate expression.
The above expression will return the sum of sales. User Filter based on Region column will not filter this aggregate formula.



