Exploring backup strategies to protect your business data
- Last Updated : October 1, 2024
- 720 Views
- 6 Min Read

Data is the driving force behind every business action, making it the most important asset for any company. With the exponential growth of digital data and its supporting technologies in the past decade, the threat to data safety has risen too. Businesses must choose from a multitude of security measures; while most of these measures ensure short-term security, data backup guarantees long-term protection.
How does data backup improve your business?
The risk of data loss is constant. With factors like hardware failures, software glitches, cyber attacks, and even natural disasters, it's more important than ever to have data backups. Creating a copy of your data can protect it from unforeseen events and ensure business continuity.

Protection in the cyberspace
Businesses in India face over 3,000 cyber attacks per week—the second most globally. With a large population and many businesses based in the country, it is imperative that organizations promptly address any event that jeopardizes their data. An effective data backup will provide a resolution regardless of whether the company uses on-premises or cloud-based storage.
Compliance, reliability, and assurance
Staying compliant increases users' confidence and encourages them to utilize the platform to its fullest extent. In fact, Article 32(2) of GDPR mentions the need to protect stored data from accidental destruction or alteration. Although the statement doesn't directly mention a backup, having one will ensure your firm's compliance with the statute. Above all, having a reliable backup option will instill a sense of confidence in customers.
Multiple options to choose from
At some point, every company needs to choose between an on-premises backup and a cloud-based backup. While both of these have their own advantages, choosing the best one comes down to understanding your company's operations.
On-premises backups
Pros:
- The primary advantage of on-premises storage is its offline availability. This ensures that connectivity issues will not stop you from accessing your critical data.
- Storage devices stay within the organization, ensuring data always stays on site.
- On-premises storage offers a high level of control. Admins can manage and alter the backups according to their policies.
- The waiting period in case of a mishap is short in an on-premises backup. The near-zero downtime for recovery improves productivity and revenue.
Cons:
- The primary drawback of any on-premises storage is maintenance cost, with frequent checks need to ensure the health of the storage systems. This also requires trained labor for maintenance, which in turn impacts revenue.
- Another con is the adverse effect in the event of a natural disaster. Incidents like fires or floods can make the on-premises servers inaccessible.
Cloud backups
Pros:
- The level of availability offered by cloud storage is huge. It allows users to access their critical data from anywhere, through any device. The only requirement is a stable internet connection.
- Cloud services need zero maintenance. Most of the activities that require user intervention can be automated in a cloud environment. For example, backups can be scheduled in advance, and the files and folders that need protection can be selected individually. This gives the user freedom to plan their actions and save time.
- The biggest advantage of using a cloud backup service is its scalability. Users can set up automatic backups without worrying about the growing size of their data. Cloud servers can promptly adapt to the increase in space and expand as your business grows.
Cons:
- Having exceptionally large amounts of data may adversely impact a company's revenue. This is due to the service's subscription fees. Companies may also have additional charges for data revival or restoration.
- Cloud backups require a stable internet connection. Any sort of connectivity issue may create a backup delay or, in some cases, loss of data during backups.
Understanding backup strategies
Having a clear idea of how backups impact your organization helps ensure business continuity and lasting, reliable professional connections. Here are five commonly used backup strategies for small-scale businesses to enterprises.
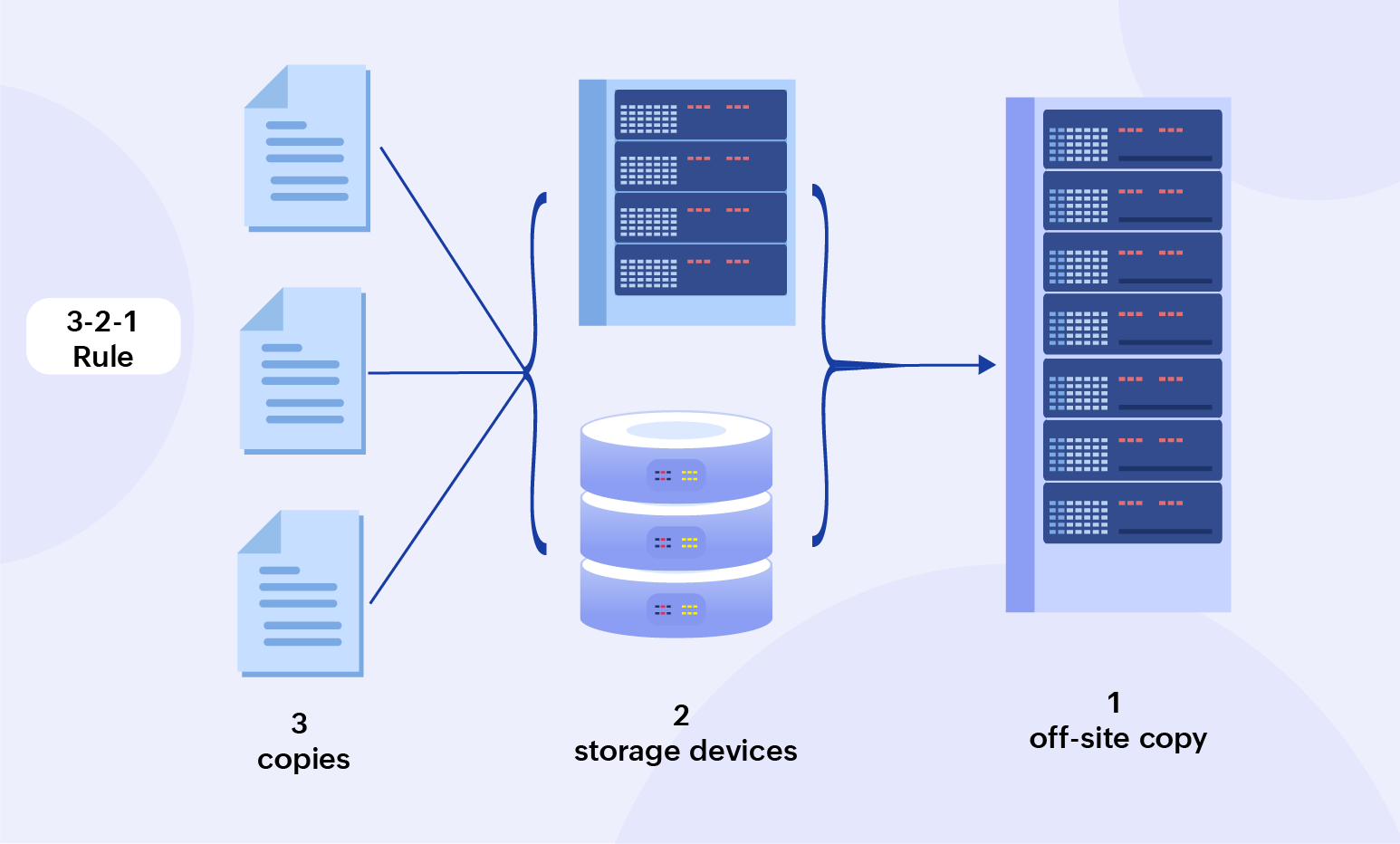
The 3-2-1 rule
A strategy that is easy to understand and implement is the 3-2-1 rule. This rule mandates maintaining three copies of the original data stored in two different types of storage devices with one copy kept off site. One big advantage of this type of backup is reliability. Having two different copies of data ensures continuity in the event of data issues.
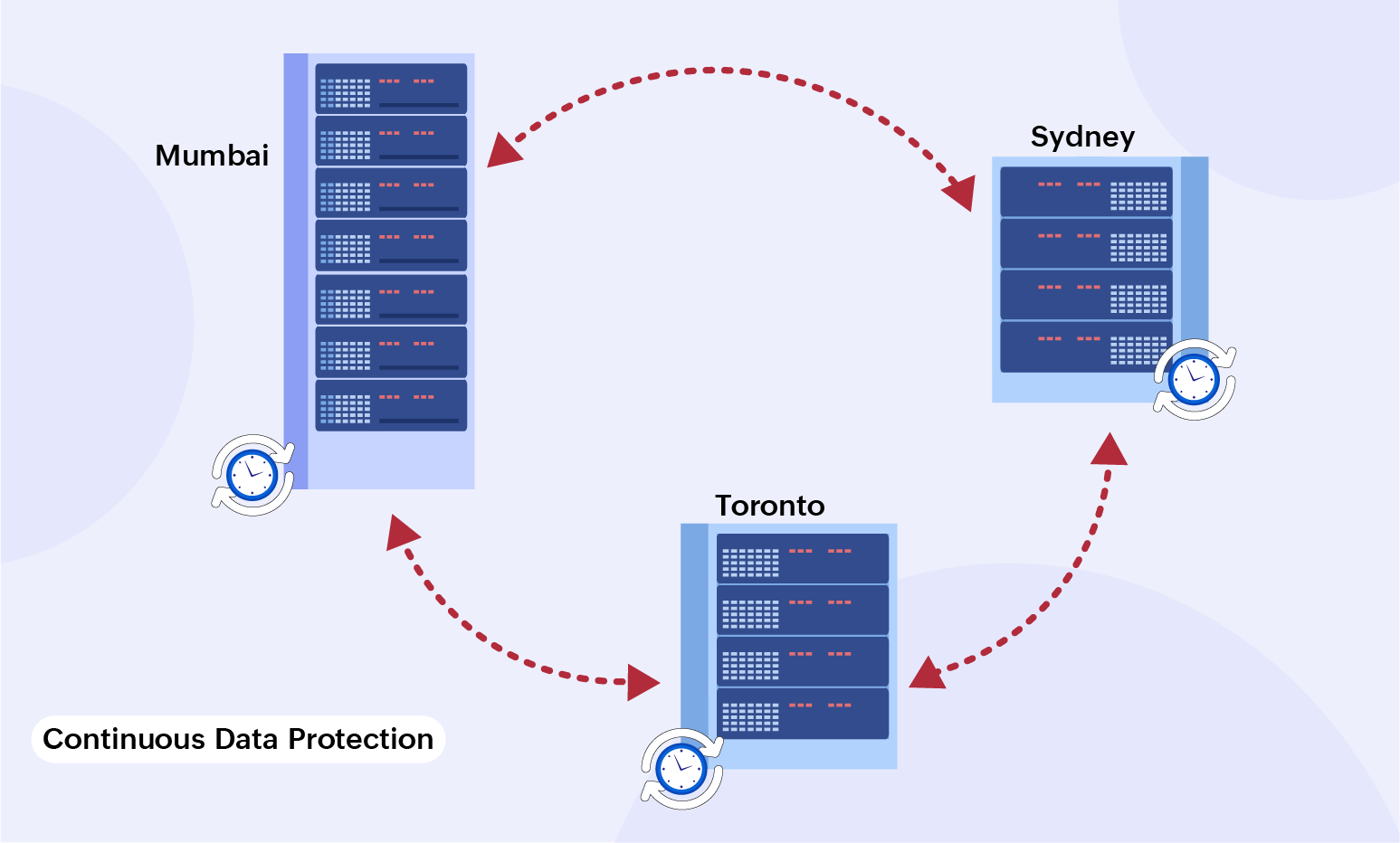
Continuous data protection
This backup solution creates data copies in real time, requiring extensive hardware for storing and networking purposes. The biggest advantage of continuous data protection is the instantaneous backup of data. Although there is a large amount of data in play, this strategy offers quick recovery in the event of a data compromise.
Granular recovery technology
The backup strategies that you have seen so far deal with holistic backup and restoration of data. When it comes to protecting critical files, users can opt for granular recovery technology. As the name suggests, this method allows you to select and back up only the files that may need to be restored. An everyday example of this is the recovery of accidentally deleted files, which is a feature in most file management platforms.
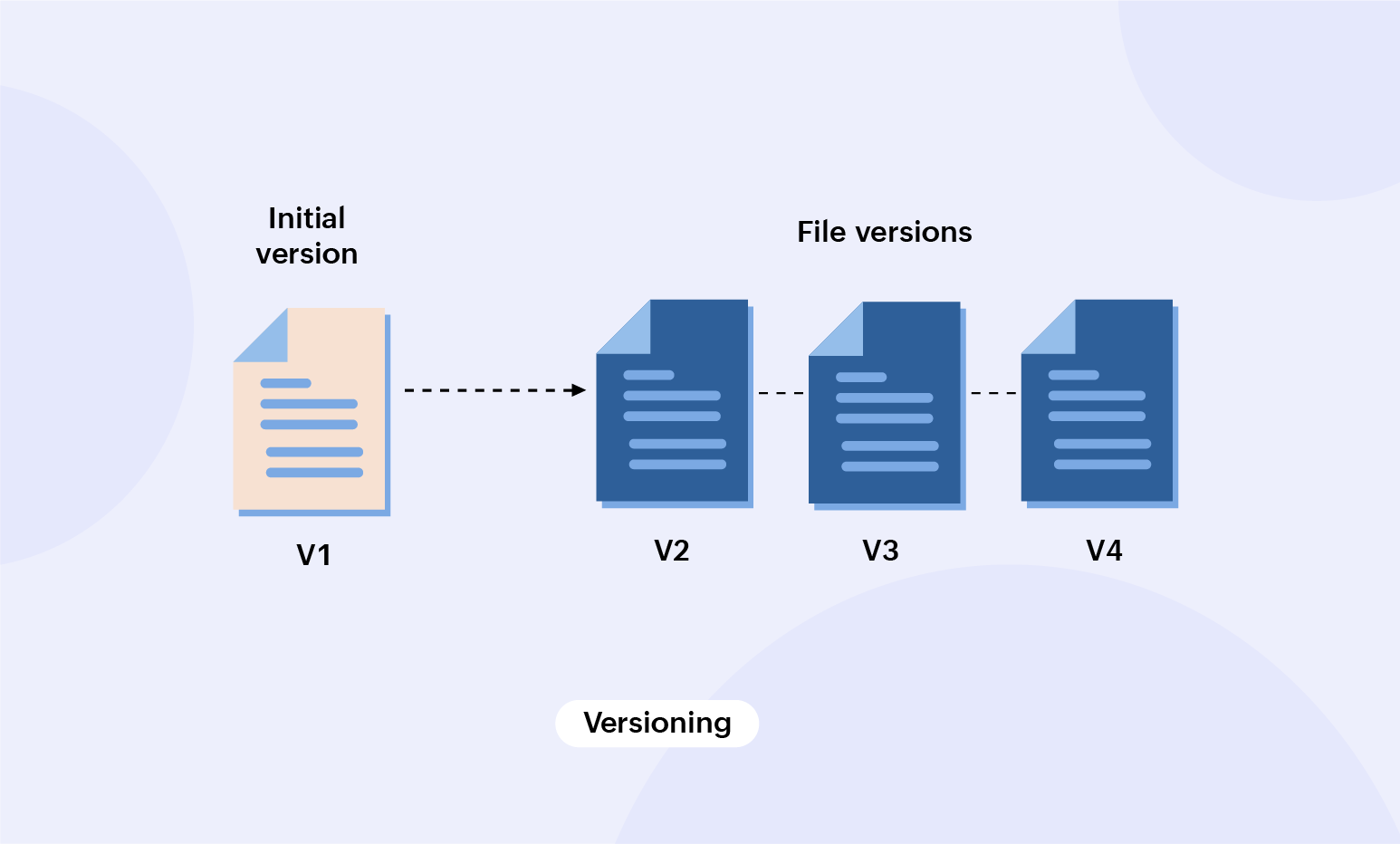
Versioning
Documents like case studies, campaign ideas, and go-to-market strategies often involve multiple people contributing to them, making tracking the document's changes difficult. That's where versioning comes in, a process where multiple versions of the same document are created over time. Although this process may seem similar to a periodic backup, the difference lies in the storage devices used. While periodic backups store the documents in a new, separate storage device, versioning creates new copies of the file on the same device.
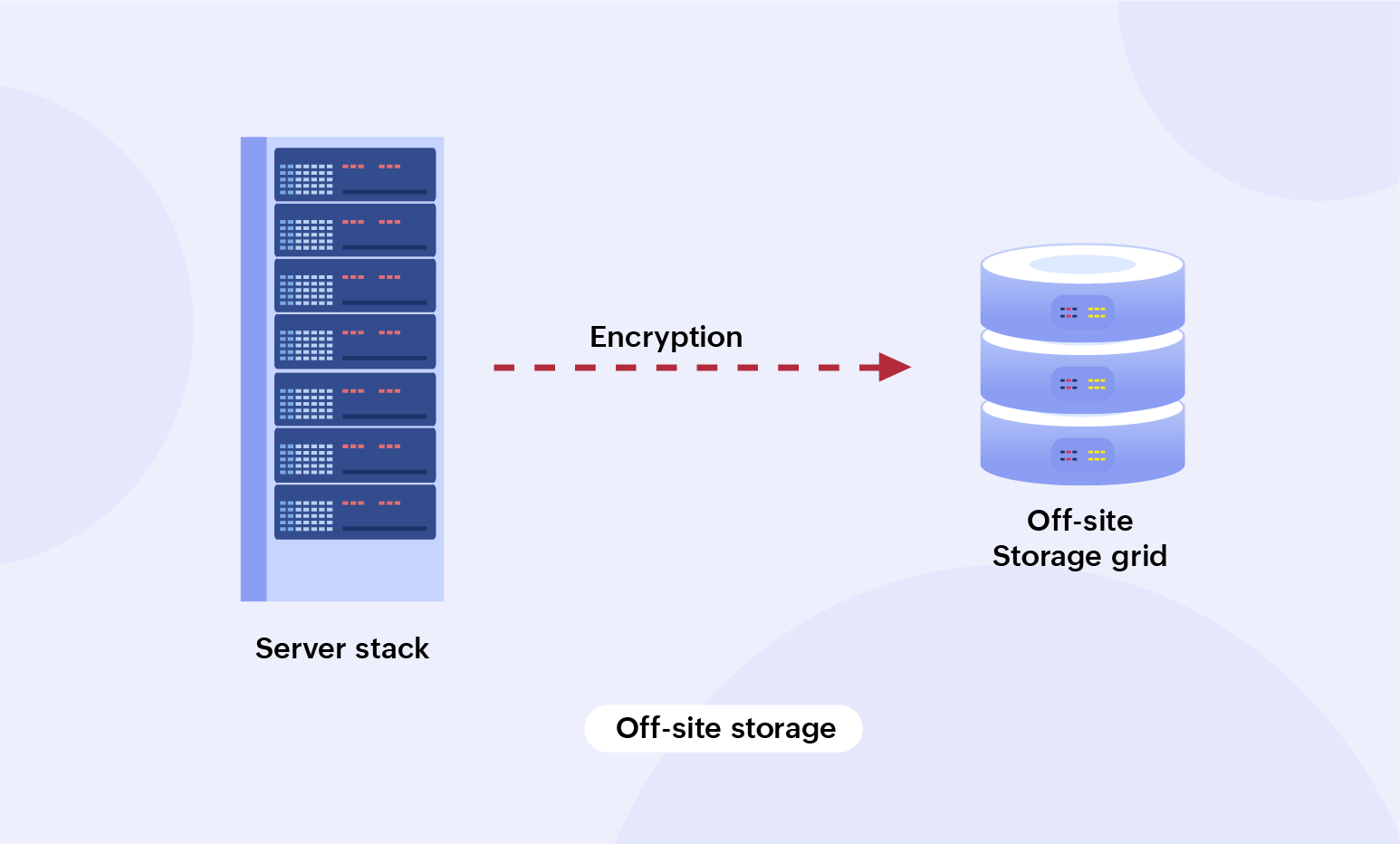
Off-site storage
This storage process involves having a copy of all your business data in a securely located backup grid away from the central server stack. A common example of this backup is cloud space. This storage strategy has two different ways to back up data—the cloud backup and the physical backup. Magnetic tapes are an example of physical backups that are still prevalent today, owing to their durability, reduced costs, and high storage capacities.
How does WorkDrive implement backups?
With a subscription to any plan on WorkDrive, you can add a backup service for all your organizational files and folders. You can also choose to download all the backup data to your local device, network attached storage (NAS), or Azure cloud storage whenever required. Backing up your WorkDrive files automatically includes data from all the Zoho applications you use, ensuring your collaborative data is always protected.
You can preview the backup files before restoring and choose which version of the backup you would like to restore. This saves storage space and gives you precise control over which version to retain. Restore single files from WorkDrive's backup for granular recovery.

When it comes to quality and metrics, WorkDrive's backup add-on, RecoveryManager Plus (RMP), ensures a low recovery time objective (RTO). This means even in the event of a data compromise, your WorkDrive data can be recovered and restored swiftly.
Another metric is the recovery point objective (RPO), which is the amount of data the company can lose without causing any damage to the business. RMP implements incremental backups, reducing the RPO significantly.
WorkDrive is GDPR and HIPAA compliant. Along with ISO 22301 certification, your organization can focus on business while WorkDrive takes care of continuity management.
The future of backups
With newer platforms coming up, backups need to store collaborative data from more than one platform. Although there are numerous ways to work around this paradigm shift, cloud consolidation is one way to retain collaborative data across multiple applications. Regardless of what method you choose, understanding the way your organization works, the amount of data collected, and the way it will be processed is making the right backup strategy.