Sales analytics 101: A comprehensive guide to key sales metrics
- Last Updated : March 21, 2025
- 275 Views
- 7 Min Read
Sales analytics is to sales, as what an expense tracker is to tracking your savings for a down payment for your dream house. Sales analytics helps you and your sales team stay on track and hit sales targets.
Running a sales team without sales analytics is akin to flying blind. Not knowing where and when to step up or pace down sales can send the sales team into a vicious cycle of disconnected actions with no idea of what works and what doesn't.
If you're overwhelmed with sales analytics and not sure about where to start, this article can help you. This blog post covers the basics of sales analytics, its benefits, and lists nine critical sales metrics that can boost your sales.
What is sales analytics?
Sales analytics is the process of analyzing sales data that has accumulated over the years to gain insights into your process, procedures, and sales performance. Sales analytics helps forecast future sales and revenue, set goals and track sales performance against goals, predict achievement, and enable course correction to hit and exceed targets.
The four types of (sales) analytics and when to use them
Sales analytics can be broadly categorized into four types:
- Descriptive analytics provides a summary of what happened in the past and what is happening now. For example, sales or revenue history. Descriptive sales analytics is helpful to discover trends, patterns, seasonal changes, and outliers in your sales data.
- Predictive analytics is the ability to foresee the future based on current performance trends. Predictive analytics is useful to make informed guesses into the future, such as expected revenue, deal propensity, agent performance, and the like.
- Diagnostic analytics is investigative in nature and aims to discover the "why" behind specific occurrences in data. It can be used to find out why trends, patterns, changes, or anomalies are observed in sales data. For example, investigating why sales increase around the last quarter of the year.
- Prescriptive analytics suggests solutions for problems and is helpful for making data-driven decisions.
Benefits of sales analytics
When implemented right, sales analytics could become the engine that powers your sales team to achieve greater efficiency and gain better rewards for sales efforts. Sales analytics can:
- Aid with everyday (tactical) and long-term (strategic) decision-making.
- Forecast sales and charter future business growth.
- Help sales leaders make better sense of sales data, interpret data correctly, and make informed decisions.
- Provide the insight for continuous process and performance improvements, such as optimizing sales strategies.
- Identify opportunities, gaps, and bottlenecks that impact overall sales.
- Help visually analyze sales cycles in a single place.
9 key sales metrics you must track
Here are the top sales metrics and KPIs (key performance indicators) to help understand and measure sales performance.
1. Sales growth
Usually measured on a year-on-year basis, sales growth charts the actual growth of a company within a given period. It's a measure of all the new sales, deals, and opportunities that the business has realized in the given period, and can determine if the business has grown or slumped as compared to the previous period.
Instead of yearly, quarterly, or monthly, sales growth can also be measured to track business growth granularly. Businesses can also measure inflation-adjusted sales growth to get a true picture of business performance.

2. Sales target
A sales target is just a goal that sales leaders set for the business. It is usually set for the year and then broken down to quarterly, monthly, and weekly targets for each region, department, or team. Based on the type and nature of the business, the sales target can be revenue numbers, number of deals, number of accounts opened, or others.
Several factors are considered before setting sales targets: overall growth plans, past revenue, market trends, team size, team performance, and geography of the business. A sales target is a critical driving force when deciding on territory management, quota management, compensation management, and formulating sales strategies.
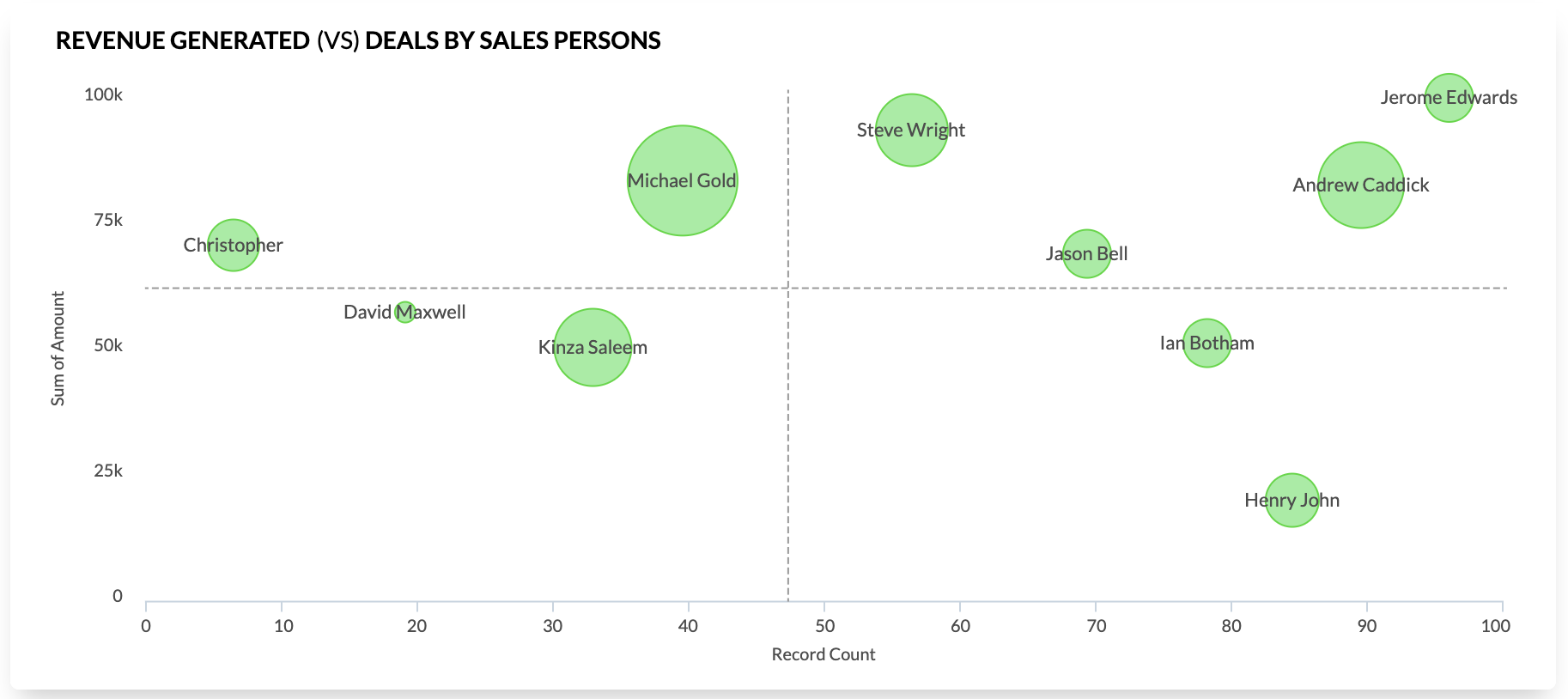
3. Sales per representative
Summing up all the sales, including new deals and accounts, recurring deals, and upgrades, brought in by each representative for the year gives you the value of sales per representative. This is useful to compare the performance of sales reps in a team within a region and to identify performance gaps and opportunities for coaching.
Sales per representative is particularly useful when comparing each salesperson's actual sales against their quota for that period.
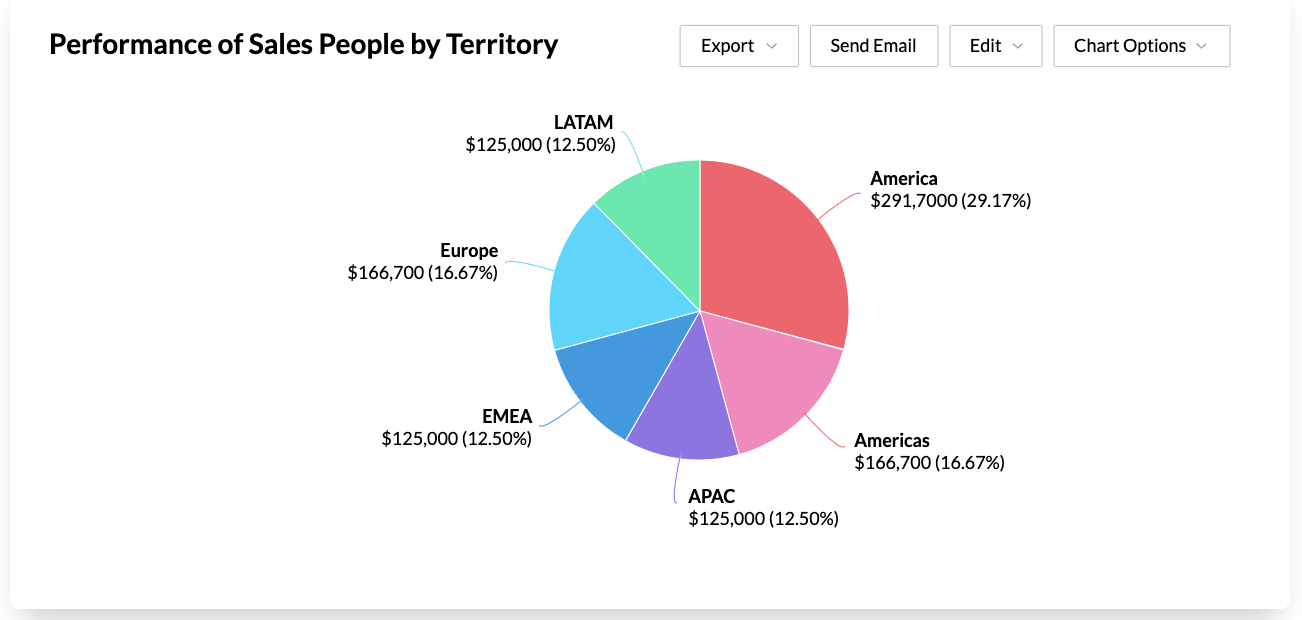
4. Sales by region
No two regions can deliver similar results. Sales by region helps understand revenue split among various regions. This knowledge helps align marketing efforts towards better performing regions and uncover reasons behind poor performance from others. Sales by region can also quickly uncover patterns in regional performance over the years. This makes it easy to detect regions where sales are slowly dipping.
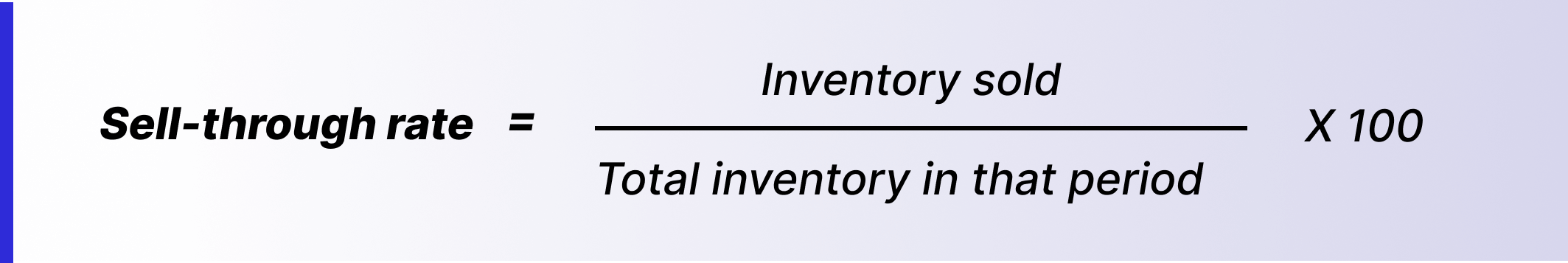
5. Sell-through rate
Sell-through rate is the percentage of inventory sold in any specific period. For businesses that sell physical products, the sell-through rate is helpful to make decisions on the supply chain, warehousing, and inventory. It paints a clear picture of how well leaders understand business cycles, demand, customer preferences, and the ability of their sales team. A higher sell-through rate indicates better planning and matching of demand and supply, while a lower sell-through rate indicates poor planning and cost drains.
6. Sales per product
Sales per product is the sum of total sales from each product. This metric helps identify the product(s) or product clusters that bring in the most revenue. It also helps spot products that need some additional sales help to promote them to customers more.
For a business that sells multiple products or services, it's unwise to have an unequal distribution of revenue from products. Any sleight of hand, such as changes in market demand, customer perception, entry of a new, better competitor, or even economic changes, can quickly dry out its revenue stream. An even distribution of revenue from multiple products ensures long-term sustainability and provides insurance against changing demands and dynamics.
7. Pipeline velocity
Similar to lead velocity, tracking sales velocity or pipeline velocity is a healthy business practice. Pipeline velocity is an indicator of how healthy your sales pipeline is and what you stand to gain out of your pipeline in an average sales cycle. This metric helps measure the number and worth of deals in your pipeline.

8. Quote to close
Sending a quote to a prospect is often just opening the door for further communication. So, measuring quote to close tells you how many deals actually convert to paying customers. This is a good metric if you're looking to understand how effectively your sales team moves prospects through the sales funnel. Although this metric alone can not be used as a measure of pipeline process health, it's a good place to start.
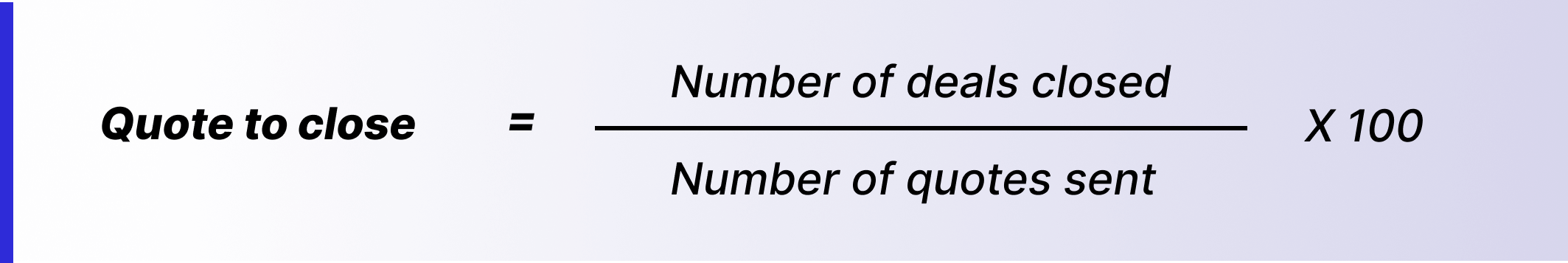
9. Average purchase value
Average purchase value or average sale value is the measure of the average value of each transaction. This metric is a great tool if you're looking to grow your business, and can highlight underlying problems in your business that might otherwise go unnoticed.
At the surface level, higher revenue figures or number of deals might indicate business growth. But looking at the average value for each sale might indicate that although you're selling more, you're actually making less when compared to historical figures. For instance, for a small business, 100 new sales and $100,000 in new revenue can seem like growth, when you've got only 50 new sales and $70,000 in new revenue in the previous year. However, if you compare the average purchase value for this year against the past (that is, $1,000 vs. $1,400), you'd realize that the business is actually slowing.
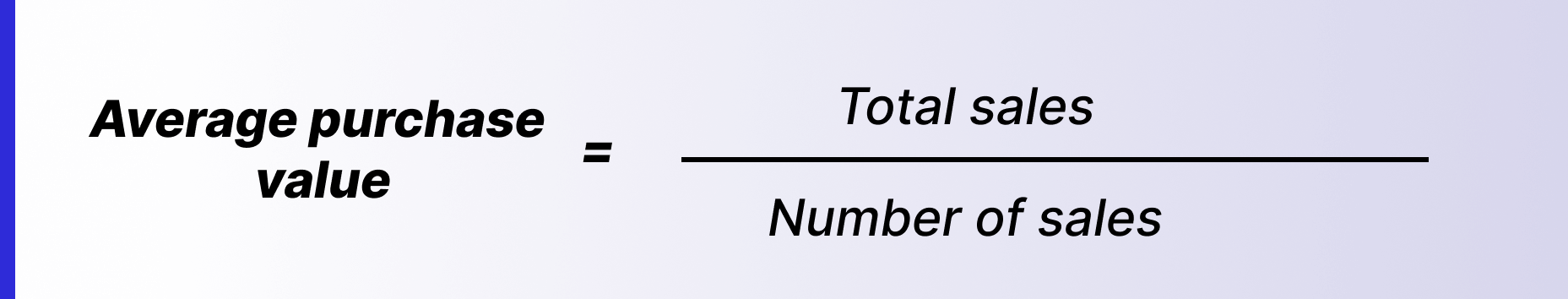
How to choose the best sales analytics software for your business
The right analytics software can help improve adoption, improve sales, streamline operations, and contribute towards improving productivity. Here's what you need to look out for when choosing your sales analytics application.
Interactive visualizations: Static reports provide information; interactive visuals enable users to go beyond surface-level analytics, dive deeper into numbers, and gain actionable insights. Look for interactions such as displaying data on hovering, drilling down into charts and reports, manipulating axes, and changing visualizations on the go.
Integrations: Rarely do organizations have sales data in a single database. Usually, sales data is strewn across CRM applications, spreadsheets, local drives, and multiple third-party tools such as billing, legal, and martech apps. Choose an analytics application that integrates with all your data sources so you can unify data and give your sales team a comprehensive view of deals and pipelines.
AI-powered insights: Applications with built-in AI can fast-track the insight gathering process and trace patterns, trends, anomalies, and outliers, which make it possible to interpret data quickly. Some analytics tools come with their own Gen-AI assistant that can summarize reports and provide conclusions.
Ease of use: Choose an analytics application that's suited for business users; one that has a short learning curve. If you can get an application retrofitted with conversational AI, that's a clear win.
Real-time updates: An expected deal didn't come through this month? Sales from a region are declining? A sudden spike in demand for a specific product? Your analytics app should be able to catch these changes as they happen and alert the entire team right away so they can act quickly.
Put your sales on turbo-drive with Zoho
Data-driven sales analytics is the future of sales. Monitoring the right sales metrics can give you a better look at your own processes, people's performance, products, and customer preferences that you can use to make better, smarter decisions focused on growth.
However, getting started with sales analytics can seem daunting. The trick is to start small and observe critical metrics that provide in-depth insight into specific areas of sales before pursuing other avenues.
Zoho CRM comes retrofitted with an expansive sales analytics feature. It enables you to create endless visualizations to track critical sales metrics like the ones discussed in this blog post. Check out Zoho CRM now.














