Baseline
A schedule baseline is an approved project plan used as a basis of comparison to the actual results. Schedule baseline is pivotal in correlating with the current performance to determine if a change, corrective action, or preventive action is necessary.
Learning Objective
Learn how to
- Determine the current project performance by comparing against initial estimates.
- Reprioritize the remaining schedule based on the comparison results.
- Accommodate the approved changes and determine the project schedule accordingly.
- Conduct scheduled reviews to determine the rate at which deliverables are produced.
Overview
An initial project consists of milestones which present many linked activities in the form of task lists or tasks. The best practice is to create a baseline of the original plan before the project execution. Create multiple baselines to compare and analyze the project changes over a given time period.
As project implementation begins, owing to unforeseen circumstances, there could arise certain change requests such as scope creep or additional requirement requests.
- These changes should be accommodated, the efforts and tasks are to be rescheduled accordingly. After this, an updated baseline should be created which reflects the current conditions.
- For complex projects, create multiple baselines as an audit trail to track the project performance due to various control changes that occur during the implementation phase.
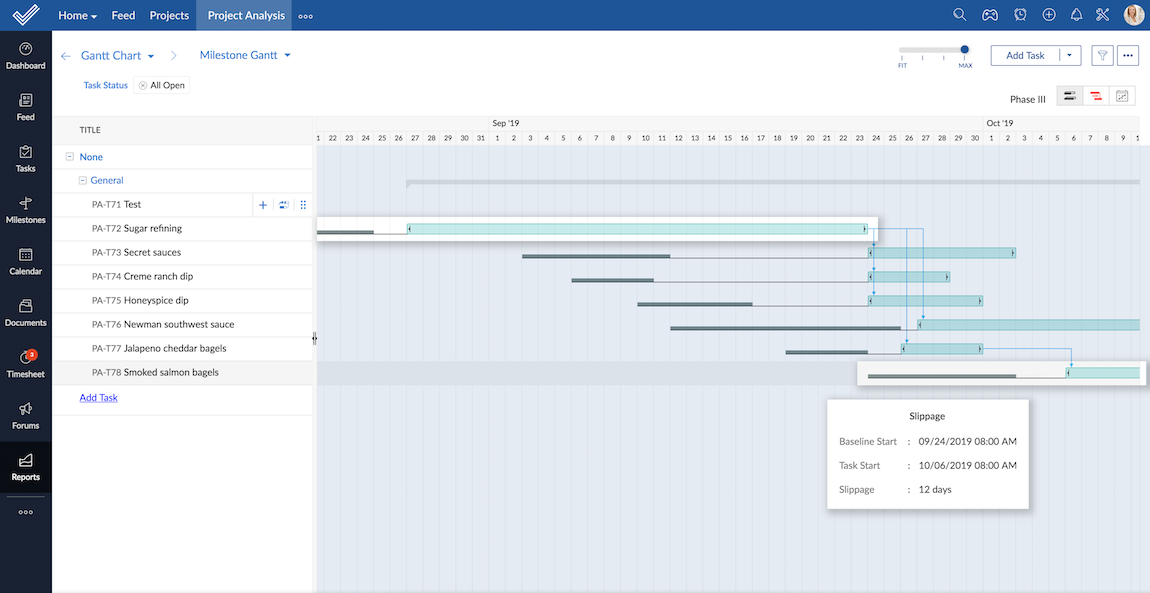
- Slippage is the difference between the baseline start date and current start date of a task. Slippage helps to keep a record of the deviation in task start dates.
- End variance is the difference between the baseline finish date and the current end date of a task. This gives the delay pattern in finish dates due to change control or due to any other unforeseen circumstances.
Scenarios
Let’s consider an instance at a food processing industry as our example. They are wholesale suppliers of bread, burgers, bagels, etc. They also produce assorted sauces and dips and supply it to restaurant outlets.
As a usual practice, before the start of each lot of their sugar production, they took a snapshot of the original project schedule by creating a Phase-I baseline. During implementation, an unforeseen situation occurred, a union strike prevented the employees in sugar refining section from performing work. Therefore, there was a delay in secret sauce production, which required the raw material (sugar) from the previous task. Also, the sauce for the burgers was not produced on time since that was also was dependent on sugar production. In addition to this, the production of a variety of dips for bagels and burgers were delayed.
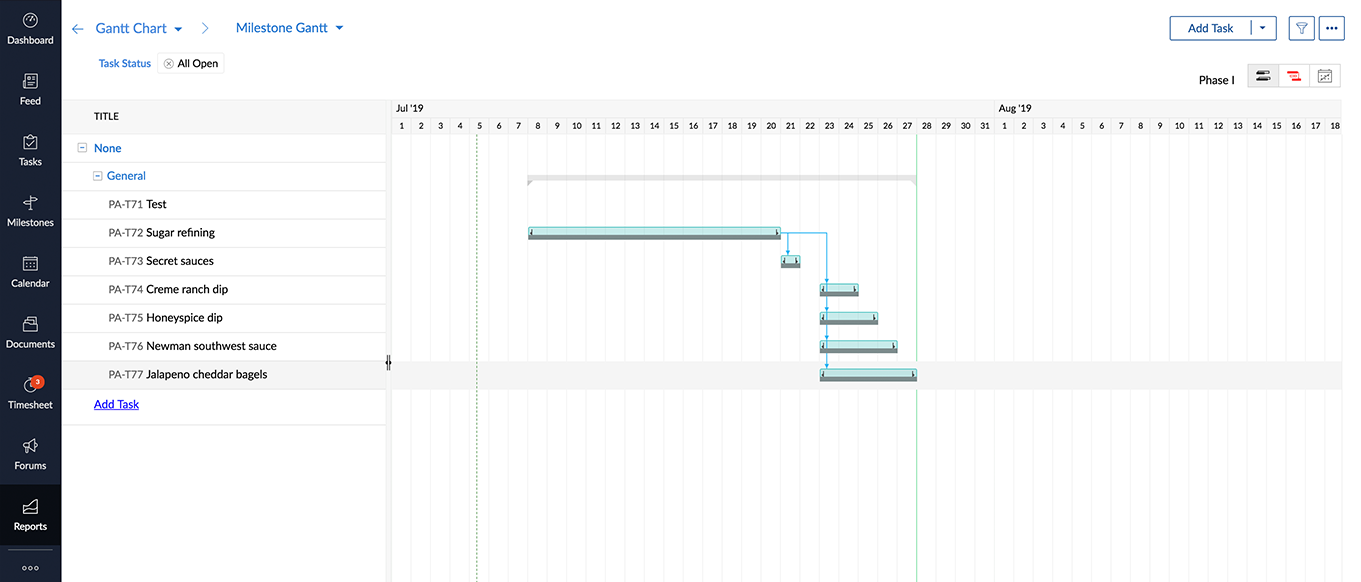
Thus project manager reschedules this task as well as the other tasks that must begin after the sugar production. Now a Phase- II baseline is created which includes the changes in schedule. Likewise, multiple baselines are created whenever an approved change is introduced in a schedule.
Finally, the project manager assesses the end variance to determine if the project is on schedule for comparison. Because of the delay in sugar production, the other dependent tasks are also delayed. Without a baseline, it is tough to spot the bottlenecks.

Slippage is the key to highlight the tasks that have a delay from their original start date. The baseline is extremely advantageous in conducting retrospectives and scheduled reviews. This helps is correcting the processes and re-organizing the tasks to ensure that the schedule is on track.