- HOME
- Taxes and compliance
- Advance tax payment: What it is and how to calculate it
Advance tax payment: What it is and how to calculate it
Advance tax is a way to pay income tax in instalments throughout the year, instead of waiting until year-end. For business owners, understanding advance tax is crucial for managing cash flow and staying compliant with tax regulations. The process is straightforward and can be completed online, ensuring a hassle-free way to meet your tax obligations.
In this guide, we’ll cover what advance tax is, its benefits, how to calculate it, and the steps to pay it.
What is advance tax?
Advance tax is the income tax you pay during the year as you earn, rather than making a lump-sum payment later. You are required to pay advance tax if your total tax liability, after accounting for TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), is ₹10,000 or more. Payments are made in instalments based on due dates set by the Income Tax Department.
Who is liable to pay advance tax?
Advance tax applies to taxpayers whose annual liability meets specific thresholds.
- Taxpayers with a liability of ₹10,000 or more
Any taxpayer—whether salaried, freelance, or business—must pay advance tax if their total tax liability for the financial year is ₹10,000 or more.
- Senior citizens (60 years or older)
Senior citizens without business income are exempt from paying advance tax. Those with business income must pay advance tax.
- Businesses under the presumptive taxation scheme (Section 44AD)
These taxpayers must pay their entire advance tax in a single instalment by 15th March, with an option to pay by 31st March.
- Independent professionals (Section 44ADA)
Professionals such as doctors, lawyers, and architects under the presumptive scheme must follow the same instalment deadlines as businesses.
What are the benefits of paying advance tax?
Paying advance tax offers financial and compliance advantages to business owners.
- Improves cash flow management: Paying taxes in instalments throughout the year helps businesses and individuals manage cash flow effectively.
- Reduces interest liability: Avoid interest charges under Sections 234B and 234C of the Income Tax Act by making timely advance tax payments.
- Avoids last-minute rush: Prevents the stress of year-end tax payments by spreading payments across the year.
- Smooth processing of refunds: Ensures faster processing of refunds for overpaid taxes through timely payments.
How to calculate advance tax?
Step 1: Estimate your income
Calculate your total income for the financial year, including:
- Interest from FDs, savings accounts, etc.
- Capital gains
- Professional income
- Rental income
- Income of minors (if clubbed with your income)
- Any other income sources
Step 2: Calculate gross taxable income
Add your salary to the income estimated in Step 1.
Step 3: Determine tax payable
Apply the applicable income tax slabs to calculate the tax on your gross taxable income.
Step 4: Subtract TDS
Subtract any tax already deducted at source or expected to be deducted.
If your net tax liability after accounting for TDS exceeds ₹10,000, you must pay advance tax in installments.
Example of advance tax calculation
Let’s understand advance tax calculation with a detailed example. Assume an individual has the following income and has chosen to opt for the old tax regime:
| Components | Amount in ₹ |
| Gross salary | 18,00,000 |
| Standard deduction | 50,000 as per the old regime |
| Net salary income | 17,50,000 |
| Interest from fixed deposits | 50,000 |
| Total income | 18,00,000 |
Applicable Section 80 deductions
| Deductions | Amount in ₹ |
| Contributions to the provident fund | 1,00,000 |
| Medical insurance premium | 25,000 |
| Total deductions | 1,25,000 |
Calculation of taxable income
| Component | Amount in ₹ |
| Total income | 18,00,000 |
| Less: Deductions | 1,25,000 |
| Taxable income | 16,75,000 |
Tax payable calculation
| Income slab | Tax percentage | Calculation | Amount in ₹ |
| Up to ₹2,50,000 | NA (Exempt) | - | 0 |
| ₹2,50,001 to ₹5,00,000 | 5% | 2,50,000 x 5% | 12,500 |
| ₹5,00,001 to ₹10,00,000 | 20% | 5,00,000 x 20% | 1,00,000 |
| Above ₹10,00,000 | 30% | 6,75,000 x 30% | 2,02,500 |
| Health & Education Cess | 4% | 3,15,000 x 4% | 12,600 |
| Total tax payable | 3,27,600 | ||
Assuming if ₹1,50,000 is deducted as TDS on salary, the individual’s net tax payable as advance tax will be:
Advance Tax = ₹3,27,600 - ₹1,50,000 = ₹1,77,600
The individual must pay ₹1,77,600 as advance tax in four installments to comply with the Income Tax Act and avoid penalties.
Advance tax due dates
The due dates and payment schedules differ based on whether you are a company, a business owner, or a self-employed individual. Here’s a breakdown of the advance tax payment timelines:
Advance tax due dates for companies
| Instalment | Due date of tax instalment | Tax amount payable |
| 1st Instalment | On or before the 15th of June | 15% of the advance tax liability |
| 2nd Instalment | On or before the 15th of September | 45% of the advance tax liability |
| 3rd Instalment | On or before the 15th of December | 75% of the advance tax liability |
| 4th Instalment | On or before the 15th of March | 100% of the advance tax liability |
Advance tax due dates for business owners and self-employed individuals
For business owners and self-employed individuals, advance tax is paid in three installments. The schedule is as follows:
| Instalment | Due date of tax instalment | Tax amount payable |
| 1st Instalment | On or before the 15th of September | 30% of the advance tax liability |
| 2nd Instalment | On or before the 15th of December | 60% of the advance tax liability |
| 3rd Instalment | On or before the 15th of March | 100% of the advance tax liability |
Advance tax due dates for individuals under the presumptive taxation scheme
Taxpayers who opt for the Presumptive Taxation Scheme under Sections 44AD (for small businesses) or 44ADA (for professionals) must pay 100% of their advance tax liability in a single installment. This payment is due on or before 15th March of the financial year.
Challan to be used for advance tax payment
To pay advance tax, taxpayers must use Challan 280. This challan is available both online and offline:
- Online: Taxpayers can access and fill out Challan 280 by visiting the official Income Tax Department portal.
- Offline: Alternatively, they can fill out the challan manually and pay the tax at designated bank branches.
How to pay advance tax online?
Paying advance tax online is a straightforward process. Here's a simple step-by-step guide to help you make the payment effortlessly:
Step 1: Visit the official e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department.
Step 2: On the left side of the screen, click on ‘e-Pay Tax’ under the Quick Links section.
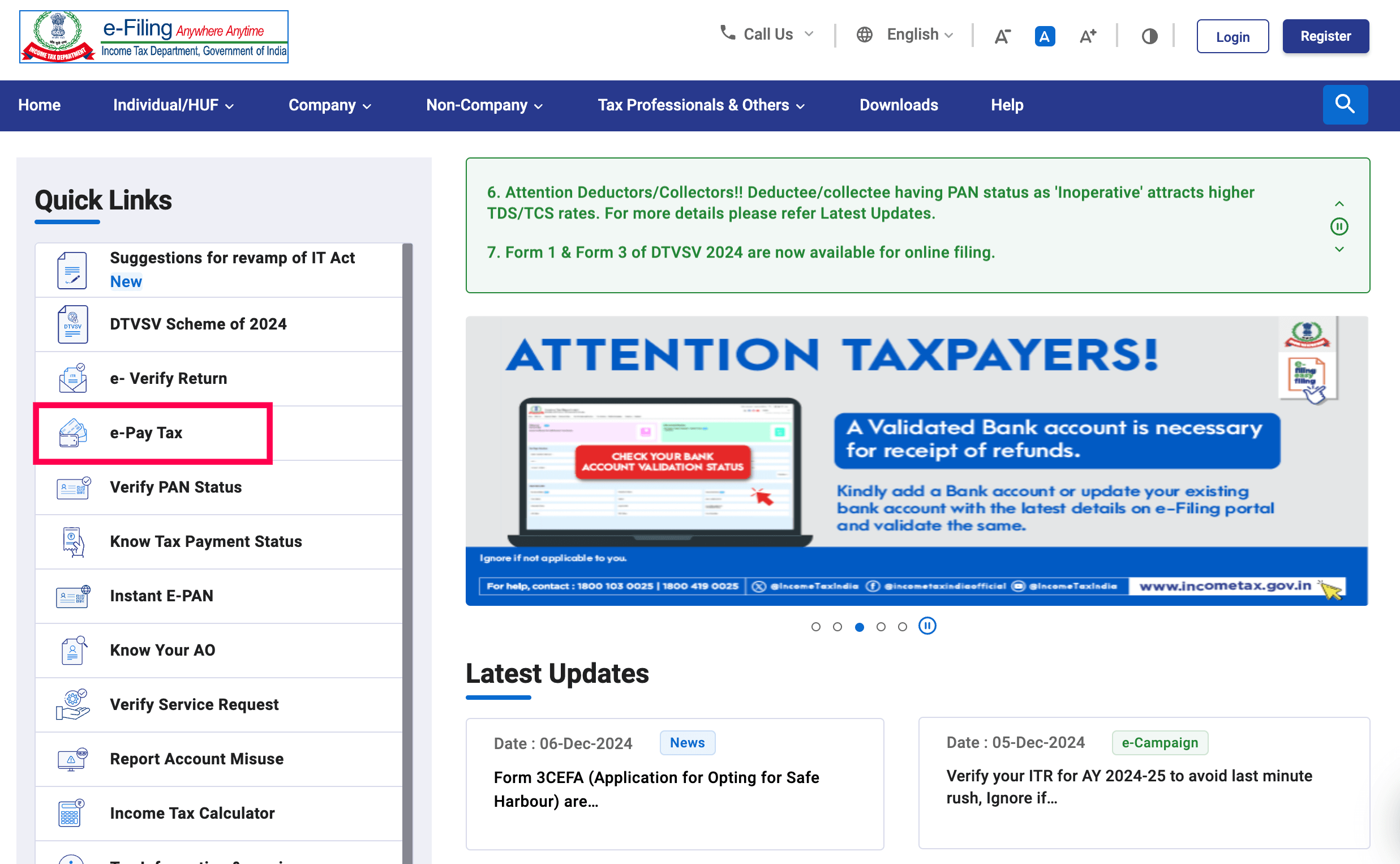
Step 3: Enter your PAN or TAN number in the required field, confirm by re-entering it, and provide your mobile number for OTP verification.
Step 4: Enter the 6-digit OTP sent to your mobile number and tap on the ‘Continue’ button.
Step 5: On the next page, click on the ‘Income Tax’ box and press the ‘Proceed’ button.
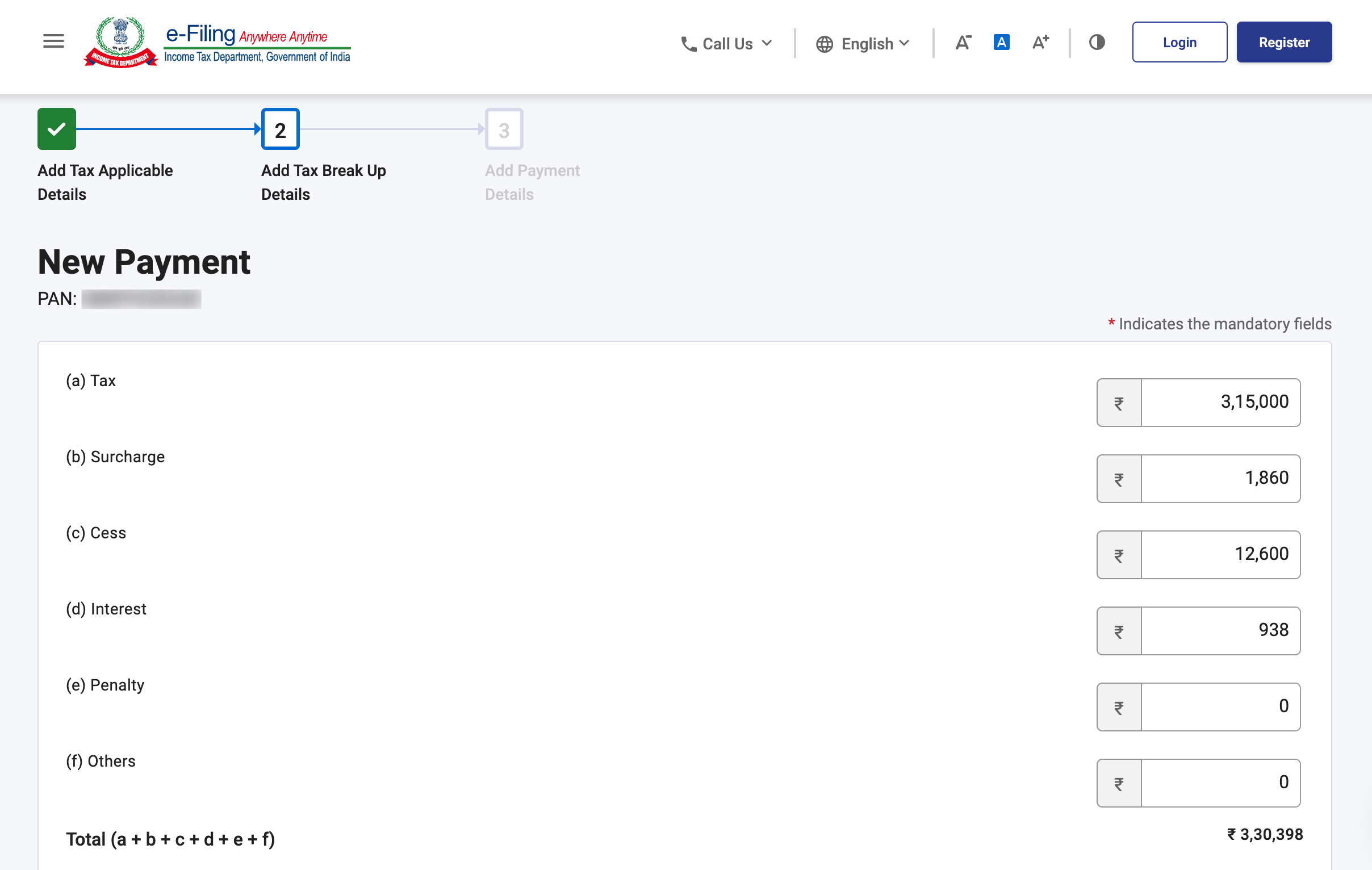
Step 6: Choose your assessment year and advance tax as your ‘Type of Payment’. Tap on the 'Continue' button.
Step 7: Next, provide all the tax details including surcharge, cess, and interest.

Step 8: Choose your preferred payment mode and bank, then click on ‘Continue.’
Step 9: Carefully review your challan details. If corrections are needed, click on ‘Edit.’ Once verified, click on the ‘Pay Now’ button.
After completing the payment, you will receive an acknowledgment slip containing the challan serial number and BSR code. You can download this Challan Form (CRN) for your records and use it when filing your income tax return.
How to check advance tax payment status?
Checking the status of your advance tax payments is an essential step to ensure your taxes are correctly credited and avoid penalties for non-payment. The Income Tax Department offers multiple ways for taxpayers to verify their advance tax payment status through the OLTAS (Online Tax Accounting System) platform. Here's how you can check it:
I. Using CIN (Challan Identification Number)
Taxpayers can verify the status of their payment by providing the following details:
- BSR code of the bank branch where the payment was made
- Challan serial number issued by the bank
- Challan tender date (the date of deposit)
- Amount paid
This information can be submitted through the Protean website (PAN & Tax Information Network Services).
II. Using TAN (Tax Deduction Account Number)
Alternatively, if you have the TAN of your deductor, you can verify the status by entering the TAN number and challan tender date. This method is simpler as it requires fewer details.
III. For banks
Banks can also check the status of challans deposited with them by selecting either the collecting bank branch or the nodal bank branch options on the OLTAS application.
Penalty and interest on late payment of advance tax
If advance tax installments are not paid by the due dates or are paid below the required percentage, interest under Section 234C is levied. This interest is charged monthly and calculated on the shortfall of the required advance tax amount.
The table below details the applicable interest rates, periods, and the calculation method for late payment or short payment of advance tax:
| Particulars | Rate of interest | Period of interest | Amount on which interest is calculated |
| If the amount of advance tax paid by 15th June is below 15% | 1% per month | 3 months | 15% of the total tax liability (-) tax paid before 15th June |
| If the amount of advance tax paid by 15th September is below 45% | 1% per month | 3 months | 45% of the total tax liability (-) tax paid before 15th September |
| If the amount of advance tax paid by 15th December is below 75% | 1% per month | 3 months | 75% of the total tax liability (-) tax paid before 15th December |
| If the amount of advance tax paid by 15th March is below 100% | 1% per month | 1 month | 100% of the total tax liability (-) tax paid before 15th March |
Key takeaways
Advance tax plays a critical role in ensuring smooth finances and compliance with tax regulations. By paying advance tax on time, companies and individuals can avoid last-minute hassles, minimize interest liabilities, and improve overall cash flow management.
The process has become simpler with online payment options, making it easier to plan finances and meet tax obligations. Regularly monitoring your advance tax payments and adhering to deadlines will keep your business or personal finances in good standing with the tax authorities.
Frequently asked questions
Is advance tax mandatory?
Yes, advance tax is mandatory. Taxpayers must pay it in four quarterly instalments between June 15 and March 15 of the financial year, as specified under Section 211 of the Income Tax Act. However, individuals using the presumptive taxation scheme are required to pay the entire advance tax amount in a single instalment by March 15.
What are the advance tax due dates for AY 2024-25?
Advance tax for AY 2024-25 must be paid according to the following schedule:
- 15th June 2024 - Pay 15% of your total advance tax liability.
- 15th September 2024 - Pay 45% of your total advance tax liability, after deducting any amount already paid
- 15th December 2024 - Pay 75% of your total advance tax liability, after accounting for previous payments
- 15th March 2025 - Pay the full 100% of your advance tax liability.
Which section of the Income Tax Act covers advance tax?
Advance tax is governed by Section 208 of the Income Tax Act, 1961. It mandates that anyone with an estimated tax liability of ₹10,000 or more, after accounting for TDS, must pay advance tax.
What is the advance tax limit?
The advance tax threshold is set at ₹10,000. If your total tax liability exceeds this amount in a financial year, you are required to pay advance tax. This applies to income from various sources such as salaries, freelance work, business profits, and rental income, after considering TDS deductions.



