- HOME
- Payroll operations
- Statutory bonus: Meaning, calculation, and eligibility rules
Statutory bonus: Meaning, calculation, and eligibility rules
A statutory bonus is a mandatory payment that employers in India must provide to eligible employees under the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965. This bonus is a way for companies to share a portion of their profits with employees, ensuring that they benefit when the company performs well.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through all you need to know about statutory bonuses, from eligibility requirements to calculation methods, to help you stay compliant and create a positive work environment.
Statutory bonus meaning
A statutory bonus is an additional payment that employers are required to provide to employees on top of their regular salary. Under the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965, employers must distribute a portion of the company’s profits to eligible employees as a recognition of their contributions.
Statutory bonus eligibility
Under the Payment of Bonus Act, every factory and establishment in India that employs 20 or more people on any day during a financial year is required to pay a statutory bonus to eligible employees.
To qualify for this bonus, employees in these organisations must meet the following criteria:
- They must have worked at least 30 days during the financial year.
- Their basic salary plus dearness allowance must not exceed ₹21,000 per month.
Initially, the government set an eligibility ceiling of ₹10,000 per month. However, with the 2015 amendment to the Act, this threshold was raised to ₹21,000 per month to better reflect salary trends.
Who is not eligible for a statutory bonus?
The following groups of employees are not eligible for a statutory bonus:
- Central and state government employees, including those in educational institutions, universities, chambers of commerce, hospitals, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and the Indian Red Cross
- Employees working in life or general insurance companies, on merchant vessels, in shipping, or as dock workers
- Employees hired through contractors
- Employees who have worked for less than 30 days in a year
- Employees dismissed from service due to riotous or violent behaviour on company premises
Employers should keep these exemptions in mind when calculating statutory bonuses to ensure full compliance with legal requirements.
Statutory bonus calculation in salary
Calculating statutory bonuses for employees is simple when you know their basic salary and dearness allowance. The bonus is typically a percentage of this combined amount, usually between 8.33% and 20%.
The bonus calculation depends on two scenarios:
Case I: For salaries up to ₹7,000
If an employee’s monthly salary is ₹7,000 or less, calculate the bonus on the actual salary amount using this formula:
Bonus = Salary X Bonus percentage (8.33% to 20%)
For example, if Employee A earns ₹4,000 per month, the minimum and maximum statutory bonus payable to them are:
Minimum bonus = 4,000 x 8.33% = ₹333.2 per month (or ₹3,998.4 annually)
Maximum bonus = 4,000 x 20% =₹800 per months (or ₹9,600 annually)
Case II: For salaries above ₹7,000
When an employee’s monthly salary is more than ₹7,000, the bonus is calculated on a base amount of ₹7,000, regardless of the actual salary. The formula to calculate bonus in this case is:
Bonus = 7,000 x Bonus percentage
For instance, if Employee B earns ₹13,000 per month:
Minimum bonus = 7,000 x 8.33% = ₹583.1 per month (or ₹6,997.2 annually)
Maximum bonus = 7,000 x 20% = ₹1400 per month (or ₹16,800 annually)
Following these steps ensures accurate bonus calculation and keeps your payroll fully compliant with statutory requirements.
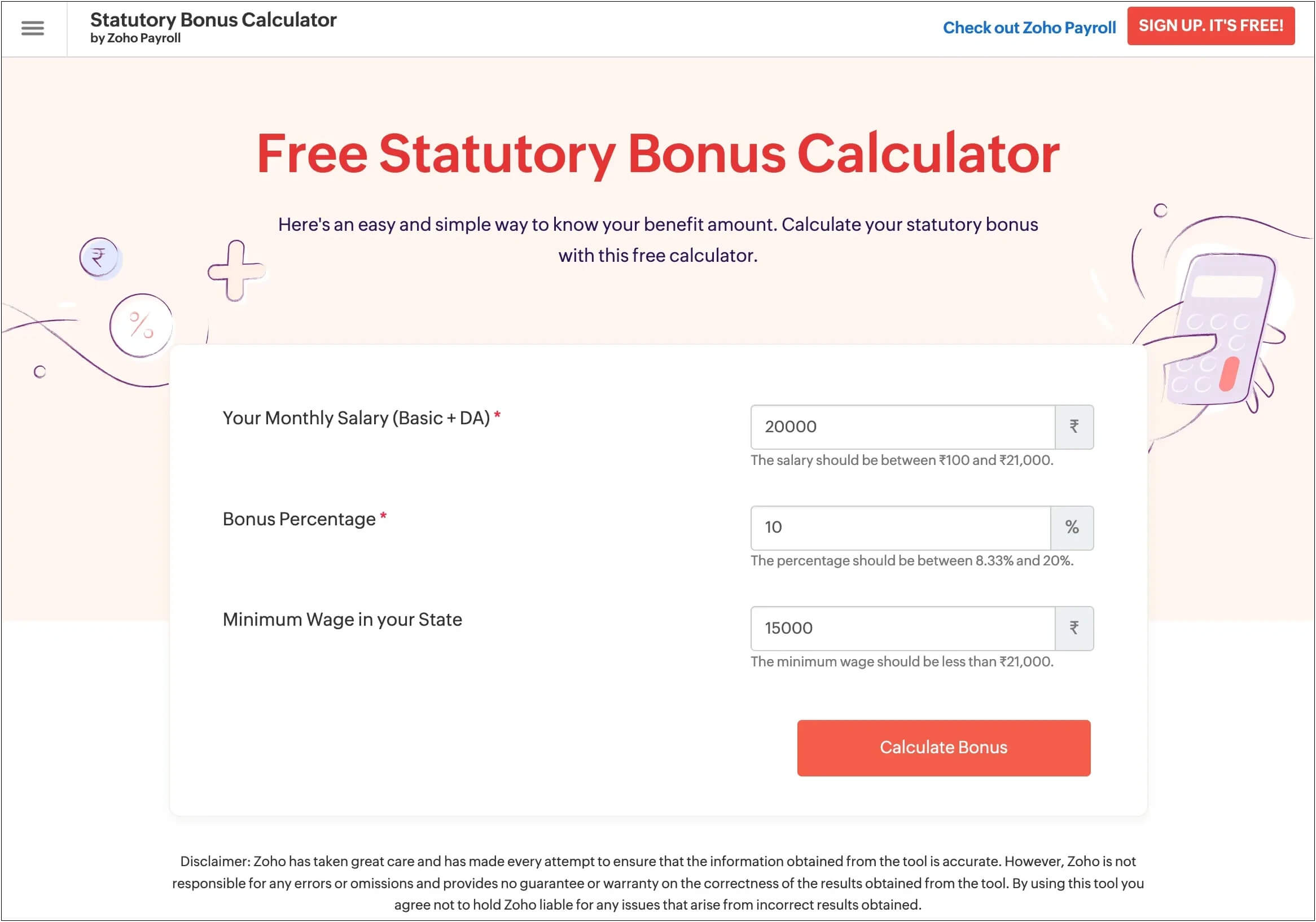
Pro tip: Use Zoho Payroll’s free statutory bonus calculator to instantly calculate bonus payouts for all your employees.
Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Enter the employee’s basic salary and dearness allowance, ensuring the combined amount is between ₹100 and ₹21,000.
Step 2: Input the bonus percentage and the minimum wage, making sure the wage is within the ₹21,000 limit.
Step 3: Click on the ‘Calculate Bonus’ button.
The calculator will display the statutory bonus amount to be paid to the employee.
When is a statutory bonus paid?
Employers are required to pay statutory bonuses within 8 months after the close of the financial year. For example, the statutory bonus for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2025, should be paid by November 30, 2025. If there is a dispute under the Industrial Disputes Act, the bonus must be disbursed within one month of the effective settlement date.
Tax on statutory bonus
According to Section 17 of the Income Tax Act, statutory bonuses are fully taxable in India. The amount received as bonus are considered a part of the employee’s salary and are included in their total taxable income.
What is an advance statutory bonus?
Some employers provide an advance statutory bonus as an incentive to motivate employees and boost performance. This advance can take various forms, such as deferred salary or an attendance bonus. Employers have the flexibility to pay this bonus either in advance or as an immediate benefit to employees.
Key takeaways
Understanding statutory bonuses is essential for employers to stay compliant with the Payment of Bonus Act, 1965. Unlike incentive bonuses, statutory bonuses are a legal requirement, reflecting a company’s commitment to sharing profits with eligible employees. Employers must be clear on eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and the impact of these bonuses on overall payroll.
To make bonus payment to your hard-working teams a breeze, use Zoho Payroll. Our cloud-based payroll software automatically calculates and disburses accurate bonuses to eligible employees, helping you meet legal requirements while reducing administrative burden.
Frequently asked questions
Is the statutory bonus part of CTC?
Yes, the statutory bonus is part of an employee’s CTC (Cost to Company). CTC includes all costs associated with an employee’s compensation, both direct and indirect. This typically includes the statutory bonus along with other components like basic salary, benefits, and employee stock options.
Who is eligible for a statutory bonus in India?
Employees earning up to ₹21,000 per month and who have worked at the establishment for at least 30 days during the financial year are eligible for a statutory bonus. Employees with wages exceeding ₹21,000 per month are not entitled to the statutory bonus.
Can organisations discontinue giving statutory bonuses to employees after some years?
No, once employees qualify for the statutory bonus, organisations are legally required to continue providing this bonus.




